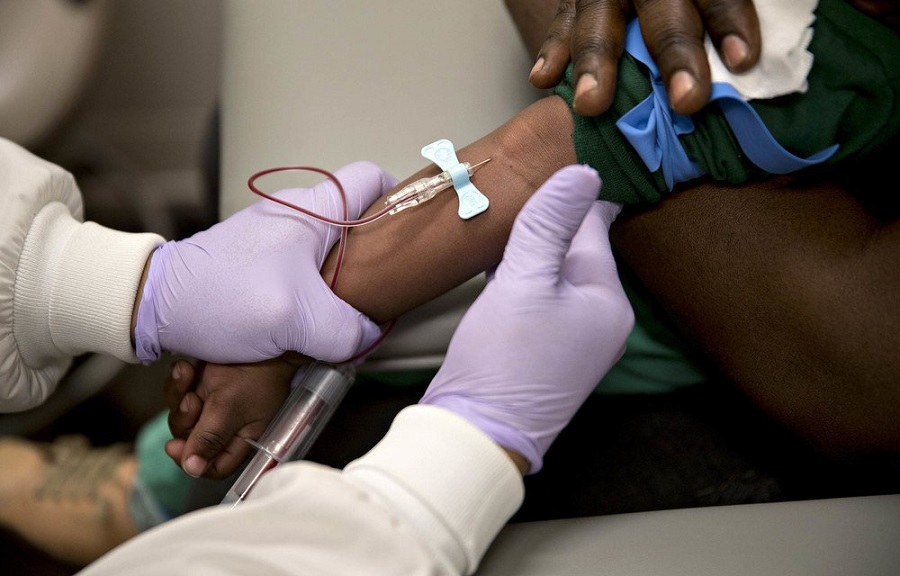
A drug named Crizanlizumab, produced by Novartis has been approved for Sickle Cell treatment in England by the National Health Service (NHS). This development has been described by the NHS as revolutionary.
Crizanlizumab, which is the first treatment for the disease, is expected to give hope to millions of people affected by the disease across the world.
Sickle Cell Disease is a genetic hereditary disorder that occurs when an individual has inherited two mutant (abnormal) hemoglobin (Hb) genes from both parents, at least one of which is HbS and the resulting symptoms and signs are due to abnormality in the shape of red blood cells.
What this means
This is a groundbreaking invention because people with Sickle cell disease have had to endure severe pain during their ‘sickle cell crisis’ which can occur multiple times in a year, often even leading to hospitalizations so they can be helped to control the pain and prevent fatal organ failure.
According to the NHS’ chief executive, Amanda Pritchard, the drug deal would help thousands of people over the next three years to have a much better quality of life.
What you should know
The drug, Crizanlizumab, made by Novartis, is injected into a vein and can be taken on its own or alongside standard treatment and regular blood transfusions.
In a trial, it was discovered that patients taking the Crizanlizumab had a crisis 1.6 times a year on average, compared to a normal average of three-time yearly.
Sickle Cell Disease in Nigeria
In Nigeria however, it is estimated that 25% of the adult population are carriers of defective S-gene as the Minister of Health, Dr. Osagie Ehanire recently disclosed that records showed that the disease affects nearly 100 million people in the world and is responsible for over 50 percent of deaths in those with the most severe form of the disease.
The Minister said sickle cell is the most prevalent genetic disease in Africa, stating that in many countries including Nigeria, 10 to 40% of the population carry the sickle-cell gene resulting in an estimated SCD prevalence of at least 2%, according to ThisDay.
Addressing the country’s high rate of SCD in the world, the Minister said, “Nigeria currently has the highest burden of Sickle Cell Disease in the whole World ahead of Democratic Republic of Congo and India, with an estimated 25% of her adult population being carriers of defective S-gene.
“WHO in 2015 estimated that 2% of new-borns in Nigeria are affected by sickle cell anaemia, giving a total of about 150,000 affected children born every year. About 50% –80% of the estimated 150,000 infants born yearly with SCD in Nigeria die before the age of five years and those that manage to survive suffer end-organs damage which shortens their lifespan including stroke.”














When is it coming to NIGERIANS
How much, and which hospital in Nigeria
Ciklavit
Ciklavit is the first indigenous nutritional supplement for the management of sickle cell anemia. A natural food extract with essential amino acids, vitamins and minerals which is derived from a species of bean seed known as Cajanus cajan and is endowed with potent anti-sickling properties.
Miracle Workers: UNIBEN Teaching Hospital cure patient of sickle cellPublished on July 19, 2012By Ifreke Inyang
When he passed out of the University of Benin Teaching Hospital clutching MBBS (Bachelor of Surgery and Bachelor of Medicine) in 1993, Dr. Bazuaye Godwin Nosakhare did not know he would be heading back to the school to help groom other doctors. He also had no inkling that 17 years down the line, he would lead a team to put the institution on the global medical map.
Inside the aircraft on a long flight to Switzerland in 2009, four members of staff of the teaching hospital comprising two nurses, one staff in the haematology department, and Bazuaye began the journey to history. At Basel, in Switzerland, they had an intensive one-year training in stem cell transplant, a relatively new branch of medicine that provides total cure for sickle cell patients, leukemia and other blood-related disorders.
When their trainers certified them fit, Dr. Bazuaye, Mrs. Imafidon Rose (pediatric nurse) Mrs. Ogunlere Beatrice (adult nurse) and Mr. Eguae Osaretin of the haematology unit returned to Benin to begin a process that makes the hospital wave the flag as a pioneer in bone marrow transplant in West Africa, coming behind Egypt and South Africa.
Something new?
Dr. Bazuaye would not be drawn into any controversy given claims by some people who say they ‘have been working on it since 2001’.
“I would rather not involve myself in any claims. I can tell you that we have successfully carried out bone narrow transplant here and the patient is alive and well. The World Health Organisation recognises it and verification teams from the Ministry of Science and Technology and Ministry of Health were here. Even the minister was here. We are not in any controversy. If anyone says he has done any such transplant, it will be nice to see the patient and see how well the patient is doing,” he says, preferring to discuss the job.
Ndik Mattew was five when his distraught parents brought him to University of Benin Teaching Hospital. He was a sickle cell patient who regularly fell ill. He was ‘problematic’ as described by the team that did the bone marrow transplant on him. He reportedly could not stand on account of stroke and paralysis. He was the shadow of a healthy when he was brought the University of Benin Teaching Hospital.
Changing from SS to AA
Shortly after the trainees returned from Switzerland Ndik became their first test.
‘It was a tough and rigorous process’ said Egua Osaretin of the hematology department who carried out countless blood tests on the patient and his elder brother whose blood came to his younger brother’s rescue. The donor was admitted for weeks so that his blood can be certified fit for his brother through radiotherapy.
The process took the hematologist to lagos endlessly given that the equipment in UBTH had not been certified at that time. When this reporter visited recently the equipment been certified. That will further simplify the process should the hospital undertake another transplant. After series of verification and a close watch that saw Dr Godwin Bazuaye living in the hospital premises for weeks, the bone marrow transplant tool place on September 28, 2011.
Ndik free from sickle cell
Dr. Nosa and his team were lent a hand by one of their trainers in Switzerland. The highly technical process simply meant that ailing Ndik’s blood was drained and replaced with that of his brother whose blood had no trace of sickle cell anemia. It is a rigorous process. Contaminated air must not slip into the patient and there must be 24-hour electricity supply, which made UBTH provide stand by power and inverter. There was no power outage, a tall order in Nigeria. But for Ndik to escape from the strangle hold of sickle cell the near impossible was done.
On completion of the transplant things began to take a turn for the better. Twelve days down the line dramatic changes occurred in Matthew’s system. The change process had commenced. His blood began to change. The SS blood group was disappearing and the AA was taking root. Expectations were that after one hundred days the injected blood would have been fully engrafted.
‘In a successful bone marrow transplant such as we did here, it is expected that in one hundred days the new blood must have been fully engrafted into the patient. That is why the search for blood donor begins from a member of the immediate family. If non is found from the family then we look out. Ndik’s elder brother came to his rescue. I believe that must have helped matters because his rate of recovery was outstanding ‘ said the Hematologist.
Six months after the hospital represented Ndik to the public. He had virtually transformed. There was no stroke or paralysis. He had begun to walk around. His elder brother had come to his rescue. As the saying goes blood proved thicker than water. Ndik’s cure had a family touch. The family is better for it. They have their son back. He has become a far cry from the sickly five- year, struck with paralysis.
Another method
Daily Sun findings showed that bone marrow or stem cell transplant is racing ahead with fresh discoveries. These days transplants can be done without a donor. An enquiry at the Moyo clinic in the United States of America with outposts in Florida, Arizona and Minnesota showed that the patient could be his donor. The hospital wrote thus:’ A bone marrow transplant or stem cell transplant, also known as a blood and marrow stem cell transplant, is a procedure that infuses healthy cells, called stem cells, into your body after you receive a course of chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy.
Your doctor may recommend a bone marrow transplant or stem cell transplant if you have a certain type of cancer, such as leukemia, or a type of blood (hematological) disease, such as sickle cell anemia. The transplant may be performed using cells from your own body (autologous transplant) or from donors (allogeneic transplant).
The system to use is contingent on the disease and the diagnosis. The heart-wrenching situation is that University of Benin Teaching Hospital is stuck. It cannot proceed with more patients in spite of an avalanche of requests. There are no back up equipments. Dr Nosa Godwin confirms that the Chief Medical Director who was away on official assignment when the reporter called had tabled requests to relevant authorities in the health sector to help procure those equipments to enable more Nigerians to benefit from the institution. Nosa has extended his call to corporate bodies to bridge the yawning gap between Nigerians and bone marrow transplant.
The Chief Medical Director of the University of Benin Teaching Hospital (UBTH), Prof. Michael Ibadin, said a 7-year old sickle cell anemia patient who had suffered stroke was the first beneficiary of the transplant after he got a match from his 14-year old brother.
“At the beginning, it was a daunting challenge because most people felt it was unassailable but the minister was convinced that we can do something when he visited last time. Here, we are looking at the beneficiary, we cannot count the cost because there is no way the patient can pay,” he said.
He said the breakthrough was achieved through a collaboration with the University of Basel, Switzerland where selected workers of the hospital led by Dr. Nosakhare Bazuaye were trained for a year.
Ibadin said the treatment would cost between N2.5 million and N5 million for a patient, but the hospital would have to be very selective in its choice of patients to reduce expected pressure and work towards acquiring more equipment for the transplant.
“The day we started, the drugs that were given to this child cost N2.1 million. It is not something you do on emergency; it is something you have to plan for. The hospital will be willing within the limits of its resources to subsidise the cost of the transplant,” he said.
“The practice of stem cell transplantation, no doubt, is capital intensive and rested on hi-tech equipment. Investment in this regard would go into thousands of millions of naira. Just for a take-off, we are starting on a small scale and have acquired only basic equipment to commence the programme,” he added.
Nigeria is the third in Africa, after Egypt and South Africa, to perform such a transplant.
https://dailypost.ng/2012/07/19/miracle-workers-uniben-teaching-hospital-cures-patient-sickle-cell/
How can a person access cure for sickle cell desease in Nigeria