A surge in fraudulent activities across banking platforms in Nigeria led to a loss of N42.6 billion by Nigerian banks in three months between April and June this year.
This was revealed by the Financial Institutions Training Centre (FITC) in its Q2 2024 Fraud and Forgeries report just released.
Without adding the Q1 record, the amount lost in Q2 2024 alone surpassed the total amount lost to fraud by the banks in the full year 2023.
Analysis of FITC’s data for last year showed that the banks lost a total of N9.4 billion throughout the year.
Quarter on quarter, the Q2 loss shows an 8,993% increase in loss when compared with the N468.4 million lost in Q1 2024. This also represents a 637% increase when compared with the N5.7 billion loss recorded in Q2 2023.
In terms of the fraud types, FITC said ‘miscellaneous and other fraud’ types constituted the largest loss, representing 96.46% of the total amount lost, with a value of N41.14 billion.
This was followed by losses from fraudulent withdrawals and computer/web fraud, amounting to approximately N781.2 million and N400.7 million, respectively.
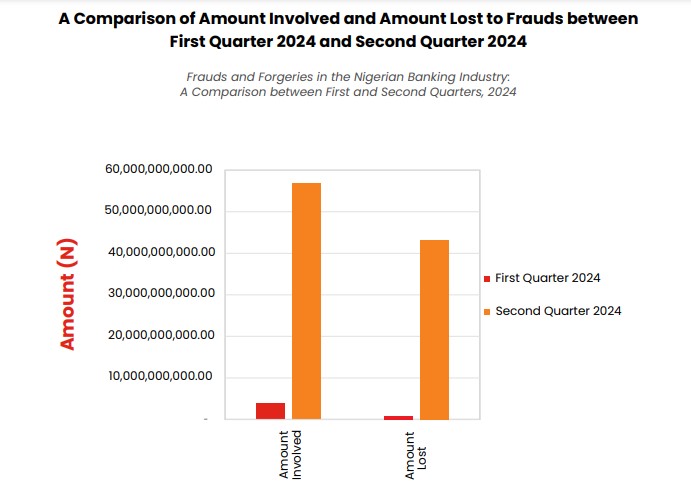
Amount involved
According to the FITC report, there was a staggering 1,784% increase in the total amount involved in fraud cases from Q1 to Q2 2024, with the sum escalating from N2.9 billion to approximately N56.3 billion in Q2.
- During the second quarter of 2024, fraudulent activities were carried out through various channels, including ATMs, online platforms like web and mobile banking, bank branches, and point-of-sale (POS) terminals.
- Among instruments used, card fraud recorded a significant decrease, declining by 47.66%. from 21,469 in Q1 to 11,237 in Q2.
- In contrast, fraudulent activity involving cheques and cash increased by 36.67% and 9.09%, respectively, with cheques surging from 30 cases in Q1 to 41 cases in Q2, while the use of cash rose from 209 in the first quarter of 2024 to 228 in the second quarter of 2024.
Loss through individual channels
A further analysis of the data shows a significant rise in the amount lost across all channels, except for mobile fraud, which recorded a decline.
- In terms of magnitude, losses through bank branch-related channels rose by 31,497%, to a value of N42.2 billion in Q2 from N133.9 million in Q1 2024.
- Additionally, computer/web frauds also saw a monumental increase of 1,560%, with losses growing from N24 million to N400.8 million.
- However, there was no indication of the amount lost due to ATM-related fraud.
- As initially mentioned, mobile fraud recorded a decline in the amount lost from the previous quarter, decreasing by 59% from N216.4 million in Q1 to N88.7 million in Q2 2024.
The need to strengthen banking platforms’ security
With the staggering increase in losses to fraud, the FITC advised the banks to enhance their monitoring and auditing procedures.
According to the Centre, deposit money institutions can utilize AI-driven tools that flag unusual entries or patterns to implement continuous and automated monitoring systems that can detect anomalies or discrepancies in settlement files.
Additionally, regular unannounced internal audits focusing specifically on settlement processes can be conducted to identify and address any irregularities promptly.
“Access controls should also be strengthened by limiting access to settlement files to only a small, vetted group of authorized personnel given the appropriate clearance and are regularly trained on the latest security protocols.
“The implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls (RBAC) can aid the reduction of the risk of unauthorized changes to settlement files,” FITC stated.
What you should know
- The FITC report is based on returns on fraud and forgery cases received from twenty-eight (28) deposit money institutions in the country.
- According to FITC, 80 of such returns were received in the quarter under review.
- Further analysis shows that twenty-six (26) reports were submitted in April, while twenty-seven (27) reports were received in both May and June.


















