In today’s interconnected world, the power of a passport extends far beyond its physical pages. It represents freedom, global mobility, and opportunities for its holders.
The Henley Passport Index, a global ranking system established in 2006 and revamped in 2018, annually evaluates and ranks 199 passports to determine the travel freedoms afforded to their bearers.
Ranking criteria
The Henley Passport Index assesses the number of destinations passport holders can access without a prior visa, termed their “visa-free score.”
- This analysis is facilitated through a collaboration with the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and utilises their comprehensive global travel database.
- With 227 potential destinations considered, the index provides a detailed look at the mobility barriers faced by citizens of various countries.
This feature article explores the passports from African nations that offer the least freedom of movement, examining the broader implications and underlying causes of their rankings.
Ten African countries with weakest passports
Africa features several countries at the lower end of the passport power spectrum.
Here are the 10 African countries with the most restricted travel freedom:
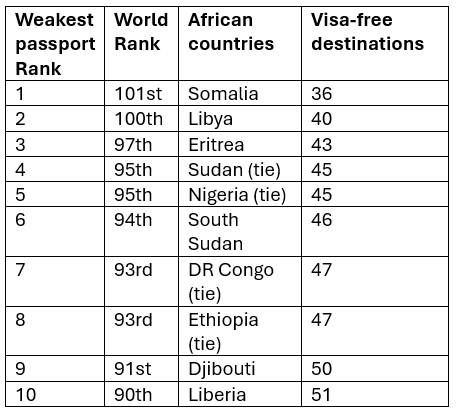
These rankings were influenced by a range of factors, including diplomatic relations, security issues, and economic stability.
Case studies
Focusing on Somalia and Nigeria, Nairametrics analysis shows the individual circumstances contributing to their low passport rankings. In Somalia, ongoing civil war and limited government infrastructure severely restrict international relationships. On the other hand, Nigeria, despite being one of Africa’s largest economies, struggles with security concerns and diplomatic isolation in some regions, impacting its international mobility.
Global context and comparison
When contrasted with countries like Germany and Singapore, where passport holders can access nearly 194 countries visa-free, the disparities in global mobility are stark. Such discrepancies highlight the need for international cooperation and support to improve passport power in underprivileged nations.
“Passports are about the reputations of nations. When your country is notorious for crimes or does not seem to make headway on issues like terrorism, you cannot expect other nations to rank you so high.
“For a country like Nigeria, there is a need for leaders to work on the country’s reputation and tackle home-grown issues,” said Joshua Balogun, an international relations analyst.














.gif)






