Article summary
- Mortgages provide opportunities for low-income earners to afford properties and achieve home ownership.
- Mortgages can serve as a tool for wealth building and long-term investment through property value appreciation and equity accumulation.
- Access to mortgages allows individuals to access capital for various purposes, establish credit history, and improve their financial prospects.
Mortgages, as a tool, can have many meanings for different people. For low-income earners with limited resources, it can mean an opportunity to purchase properties that they otherwise would not be able to afford.
This enables people and families to accomplish the goal of home ownership, which is frequently regarded as a fundamental component of livelihood in many cultures. Mortgages are tools for developing wealth and financial security for investors. By leveraging borrowed funds to purchase a property, investor benefits from the property’s value appreciation over time, which can lead to equity accumulation and a long-term investment.
For other people, mortgages provide access to capital. Mortgages can offer borrowers access to large sums of capital that can be used for a variety of objectives, including supporting schooling, starting a business, making home upgrades, or consolidating debts. Individuals can establish their credit history and increase their credit score by properly managing a mortgage and making regular, on-time payments.
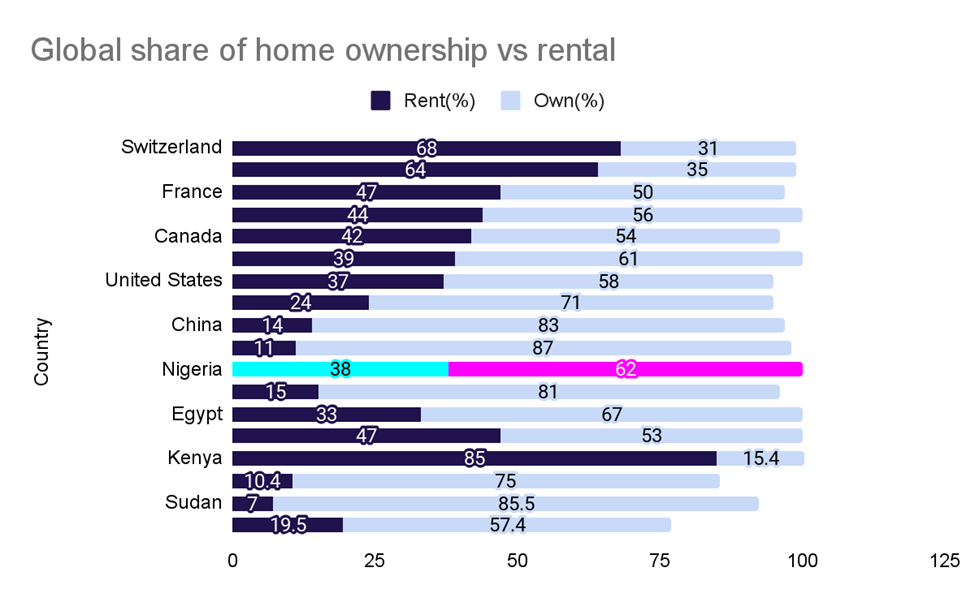
A higher credit score can lead to cheaper borrowing costs, easier access to credit, and better financial chances in the long run. All over the world, 97% of the money in the financial market is created through debt, so, however you look at it, mortgages are extremely important to a working financial system. A working mortgage system usually encourages home ownership. Countries with a higher mortgage penetration rate, naturally have more homeowners than renters.
Mortgages are important for individuals, the real estate industry, and the broader economy, whether you are looking at it as an individual, a government, or a business. Mortgages facilitate property transactions and generate income for real estate agents, mortgage lenders, appraisers, and other professionals involved in the transaction. The availability of mortgage finance can boost economic growth by raising consumer spending and stimulating real estate investment. But more than this, mortgages have more benefits for the government. For instance, it costs the government more to have a working mortgage system than it benefits the nine to fiver who needs it to purchase their first home.
Historically, Nigeria’s mortgage system has been seen as underdeveloped for a variety of reasons. Economic and market challenges, including limited access to finance, high-interest rates, stringent lending criteria, and the requirements for substantial down payments, are some of the barriers that have hindered a number of potential mortgage beneficiaries from obtaining mortgages.
There are several reasons why mortgage markets are important for most governments. One of the most referenced is meeting the social objective of providing shelter for all. For instance, in 1994, the Federal Government of Nigeria instituted the Federal Mortgage Bank of Nigeria (FMBN) as the apex mortgage institution in Nigeria. Through the National Housing Fund (NHF), the FMBN is charged with mobilizing funds for the provision of “affordable” residential housing for Nigerians. This is in line with meeting the nation’s social policy objective of providing housing for all.
Aside from meeting social needs, what else do mortgages do for the government, and how can Nigeria enhance mortgage penetration?
More than a social need, the provision of mortgage facilities for housing development has enormous benefits for the government. One of the most important benefits is that it will provide a potent line for revenue generation. The Nigerian government can build its mortgage system as a revenue-generating mechanism.
Through fees, interest payments, and other revenue streams associated with mortgage lending, governments have the opportunity to generate income that can be used to support other programs or services. But how can this be realistically achieved? In our thoughts, two things can be done. On the one hand, fix the regulatory issues around mortgages, and on the other, fix mortgage accessibility and affordability problems.
Improve the legal and regulatory framework
The Land Use Act of 1978 was promulgated primarily to consolidate the numerous land ownership systems that existed in the country. With respect to the mortgage system in the country, many of the lapses in the legal framework are processes related. To enable a vibrant mortgage system, Nigeria needs to strengthen its legal and regulatory framework for mortgages, including property rights, land registration, and foreclosure procedures. Clear and unambiguous property rights, fast land registration processes, and well-defined foreclosure procedures can give lenders and borrowers better security, perhaps leading to additional mortgage lending.
Increase access to affordable financing
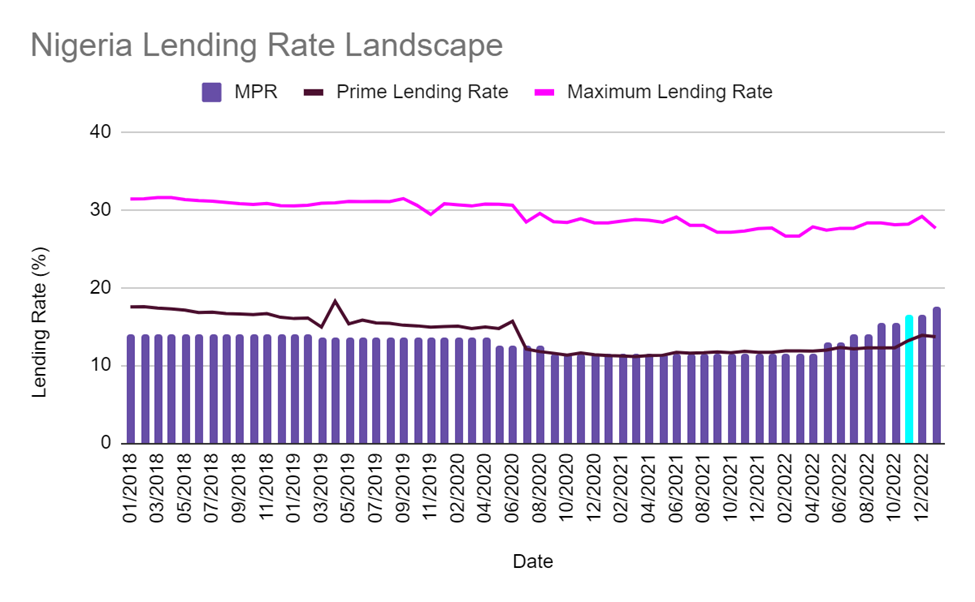
Between 1977, when the Federal Mortgage Bank was established, and January 2019, when the FMBN’s digital platforms were launched in Abuja, the bank had only disbursed N193.4 billion worth of mortgages to 18,935 Nigerian workers. Although the disbursement value improved to N298 billion in 2020, the total disbursement to date has been reportedly poor compared to expectations, a figure that real estate professionals described as a drop in the ocean. To date, one of the biggest factors contributing to low mortgage penetration in Nigeria is the high cost of borrowing. Since 2018, the monetary policy rate has hovered between 14% and 17.5%. This high rate of interest has historically waned the attractiveness of mortgages in Nigeria, leading to low adoption.
Nigeria can make more affordable financing choices available to homebuyers. This can be accomplished through efforts such as government-backed mortgage guarantee schemes, which decrease lender risk and encourage lenders to offer mortgage loans to a broader spectrum of borrowers, including those with lower incomes or limited credit histories. Reducing the cost of mortgages automatically increases their attractiveness, which will result in higher rates of mortgage penetration. Let us know other reasons why Nigeria needs to build its mortgage system.














